
It is crucial to begin memoing at the onset of research. Qualitative research is inherently reflexive as the researcher delves deeper into their subject, it is important to chronicle their own thought processes through reflective or methodological memos, as doing so may highlight their own subjective interpretations of data. Memos Ĭreating memos during the coding process is integral to both grounded and a priori coding approaches. The process generally involves identifying themes from the existing codes, reducing the themes to a manageable number, creating hierarchies within the themes and then linking themes together through theoretical modeling.
Qualitative codebook example software#
Some examples of qualitative software packages include Atlas.ti, MAXQDA, NVivo, QDA Miner, and RQDA.Īfter assembling codes it is time to organize them into broader themes and categories. The process can be done manually, which can be as simple as highlighting different concepts with different colours, or fed into a software package.
Qualitative codebook example code#
Iain Hay (2005) outlines a two-step process beginning with basic coding in order to distinguish overall themes, followed by a more in depth, interpretive code in which more specific trends and patterns can be interpreted. In social sciences, spreadsheets such as Excel and more advanced software packages such as R, Matlab, PSPP/ SPSS, DAP/ SAS, MiniTab and Stata are often used.įor disciplines in which a qualitative format is preferential, including ethnography, humanistic geography or phenomenological psychology a varied approach to coding can be applied.
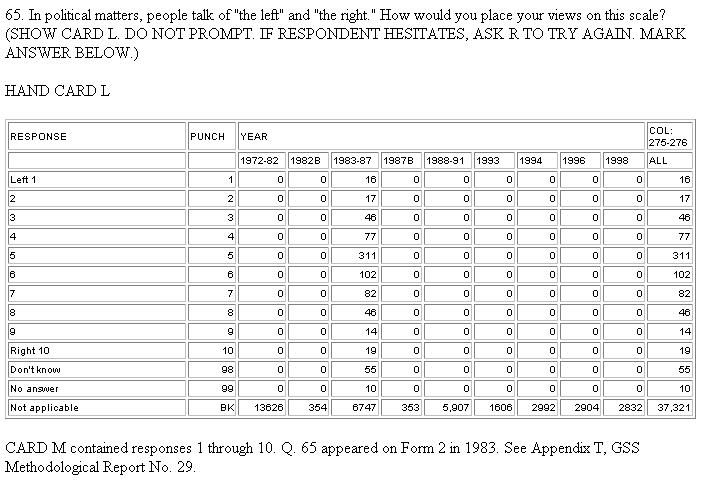
Note that some of the above are not mutually exclusive. Questionnaire data can be pre-coded (process of assigning codes to expected answers on designed questionnaire), field-coded (process of assigning codes as soon as data is available, usually during fieldwork), post-coded (coding of open questions on completed questionnaires) or office-coded (done after fieldwork). There should be clear guidelines for coders (individuals who do the coding) so that code is consistent.įor quantitative analysis, data is coded usually into measured and recorded as nominal or ordinal variables. One code should apply to only one category and categories should be comprehensive.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
